

Among the Monel nickel-copper alloy family, there are two alloys that look very similar in appearance, namely Alloy 400 and Alloy K500. A closer inspection reveals some differences between the two. A further explanation of these differences may be helpful in material selection issues. In this article, we will explore these two alloys and compare and contrast their metallurgical properties.
2025-10-29 17:53:14
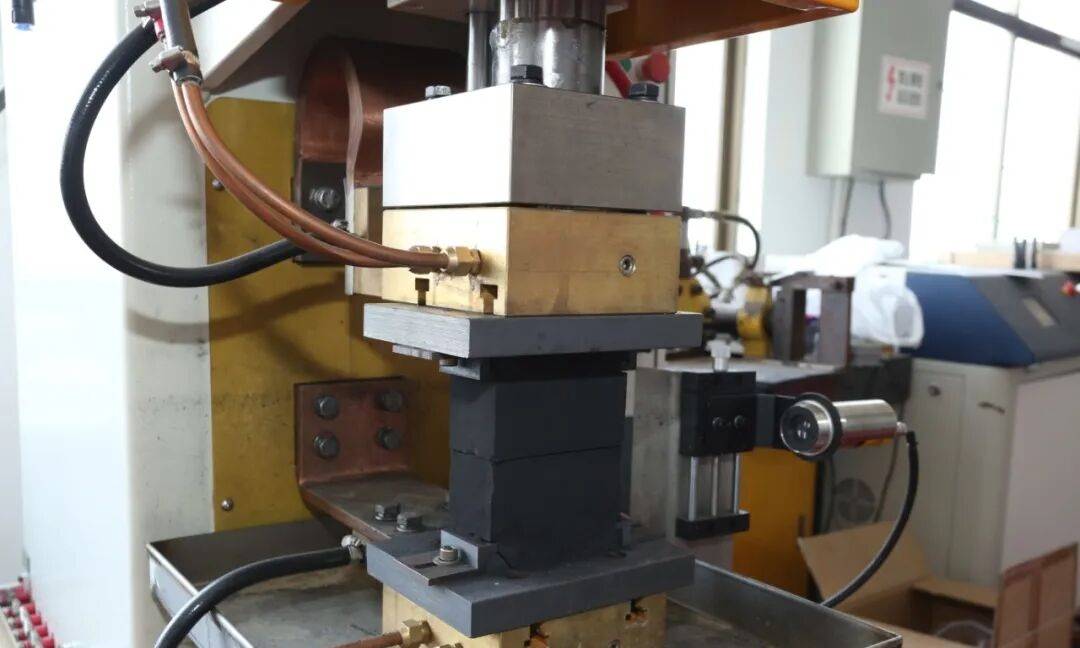

Diffusion welding is a solid-state welding method that forms a strong connection by making the surface atoms of the welded parts diffuse into each other under high temperature and pressure. It is suitable for dissimilar metals, heat-resistant alloys, ceramics and other materials, and has the advantages of high joint strength and small deformation.
2025-10-29 17:50:23

To ensure the product quality of wind power castings and meet the low-temperature impact performance in the as-cast state, it is necessary to make the ferrite matrix and spheroidization effect of the castings meet the standard requirements. This paper takes the medium-frequency induction furnace melting as the premise, combines the self-hardening furan resin sand molding process, and produces wind energy castings with a mass of 7500kg and a maximum wall thickness of 150mm. It analyzes the organizational control measures in the production process of large-section castings and discusses how to achieve the batch production of ferrite matrix ductile iron through the reasonable selection of chemical composition and effective control of the spheroidization and inoculation process.
2025-10-28 17:58:32
High-temperature bluing/blackening (alkaline oxidation method)
2025-10-28 17:51:08

In fields such as new energy vehicles, consumer electronics, and industrial equipment, die-cast parts have become the main structural components due to their three major advantages: high production efficiency, integrated molding, and lightweight. However, many engineers often fall into a trap when designing - they only focus on strength and size, while neglecting surface quality. In fact, surface defects not only affect appearance but may also cause assembly jams, corrosion failures, and even functional abnormalities.
2025-10-28 17:47:32

In contemporary manufacturing and product creative design, surface treatment technology plays a crucial role. It not only significantly enhances the aesthetic appeal and durability of products but also endows them with a series of specific functional characteristics.
A wide variety of materials are used in the surface treatment process, each with its unique properties and application fields. This article aims to provide an in-depth explanation of several widely used surface treatment materials and their performance in practical applications.
2025-10-28 17:41:30

Stainless steel passivation treatment enhances corrosion resistance by forming a dense oxide film on the surface (such as Cr₂O₃). The impact of this treatment on electrical conductivity needs to be systematically analyzed from three dimensions: material properties, film structure, and process parameters.
2025-10-23 19:35:37

Between the vast blue sky and the deep space, every breakthrough of aircraft is inseparable from the innovation of material technology. There is a kind of metal material, with its core strength of being lightweight, high-strength and resistant to extreme environments, has become a "hot commodity" in the aerospace field. It is the TB5 titanium alloy (Ti-15V-3Cr-3Sn-3Al). From the key structures of fighter jets to the core components of satellites, its presence is everywhere, silently safeguarding every flight and exploration.
2025-10-23 19:33:19
In this era of pursuing efficiency and environmental protection, lightweighting has become a key direction for the development of many industries. From automobiles to aerospace, from electronic devices to medical equipment, reducing product weight not only lowers energy consumption and enhances performance but also contributes to sustainable development. In this race for lightweighting, magnesium alloys, with their unique advantages, have become the highly anticipated "star material".
2025-10-23 19:32:05
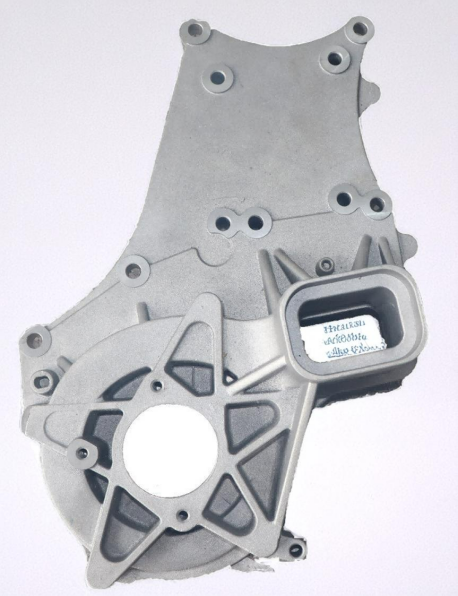
The rear cover is a key component in the construction of hydraulic motor systems and hydraulic pump systems for excavators, and the innovation and breakthrough in its casting process pose a major challenge. Without high-quality rear covers, the construction of high-quality hydraulic systems will face significant difficulties. The rear cover made of ductile iron has high requirements in terms of dimensional accuracy, inner cavity cleanliness, and material consistency. Therefore, when the company first produced this type of product, the difficulty of process research and development was relatively large. Recently, we produced a rear cover (as shown in Figure 1), with a weight of 77 kg, the maximum contour size of the casting is 342mm×303mm×137.5 mm, and the material is ductile iron. The wall thickness is relatively large, with the maximum wall thickness being 137.5 mm. The main structure includes two high-pressure oil channels and one oil suction channel. The core size of the oil suction channel is relatively large, with a diameter of 87 mm, a length of 130 mm, and a height of 137.5 mm, as shown in Figure 2.
2025-10-21 18:41:29
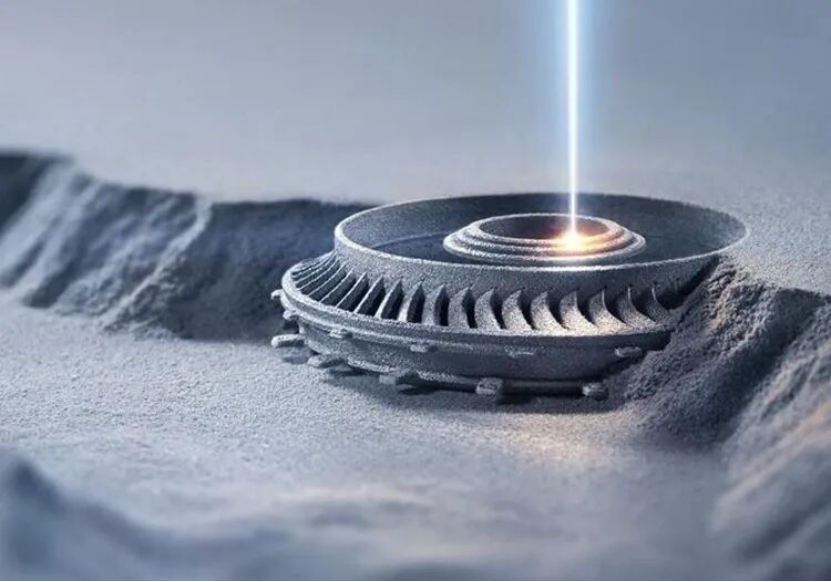

Among numerous metal materials, titanium alloy is undoubtedly the synonym of "high value". It combines high strength with lightweight characteristics, with a strength close to that of steel but a weight reduction of about 40%. Additionally, titanium alloy also has excellent corrosion resistance and high-temperature resistance, and thus has been widely used in fields such as aerospace, medical care, and automobiles, where material performance requirements are extremely strict. However, this metal also has its drawbacks, namely, high processing difficulty. Due to its poor thermal conductivity, traditional cutting processes can easily cause overheating or even damage to the cutting tools, resulting in low processing efficiency and significant material waste. This is why 3D printing is regarded as a more ideal processing method.
2025-10-21 18:35:11
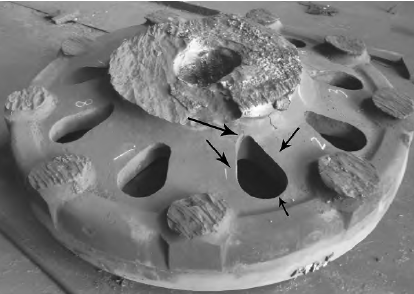
High manganese steel mainly refers to a material that rapidly hardens on the surface of steel structures under large impact loads and has wear resistance. The slower the crack propagation speed during its long-term use, the lower the probability of safety accidents. Currently, high manganese steel castings are widely used in multiple industries. Due to the larger linear shrinkage parameter and smaller heat transfer coefficient of high manganese steel compared to carbon steel, during the solidification and heat treatment of high manganese steel castings, high thermal stress is easily generated due to uneven temperature distribution and large temperature differences in the castings, causing crack problems. Especially for complex high manganese steel castings with a thickness of over 120mm, it is difficult to control the crack problem during production.
2025-10-21 18:33:12
367



