

Rolled products and small forgings processed under pressure are prone to obtaining fine and uniform austenite grains. Parts made from such billets and subjected to quenching and tempering treatment (provided that the raw materials and heat treatment processes are normal) usually achieve fine grains of grade 8 or above, which are relatively uniform. However, large forgings are different. G. Bendel et al. 24 took radial and axial samples from oil-quenched and tempered generator shafts (28NiCrMo74), turbine rotors (21CrMoV51), and other large forgings of different steels. They studied the metallographic structures of nearly 200 samples from 100 forgings (with diameters ranging from 400 to 1400 mm, forged from 100 to 150-ton steel ingots) using picric acid and additives to reveal austenite grains. The results showed that the austenite grains of all 200 samples were within the range of 0 to 7 grades, with 3 to 4 grades (excluding those smaller than 3 grades) accounting for 50%. We have also encountered similar situations in the production of large forgings.
2025-11-25 13:55:14
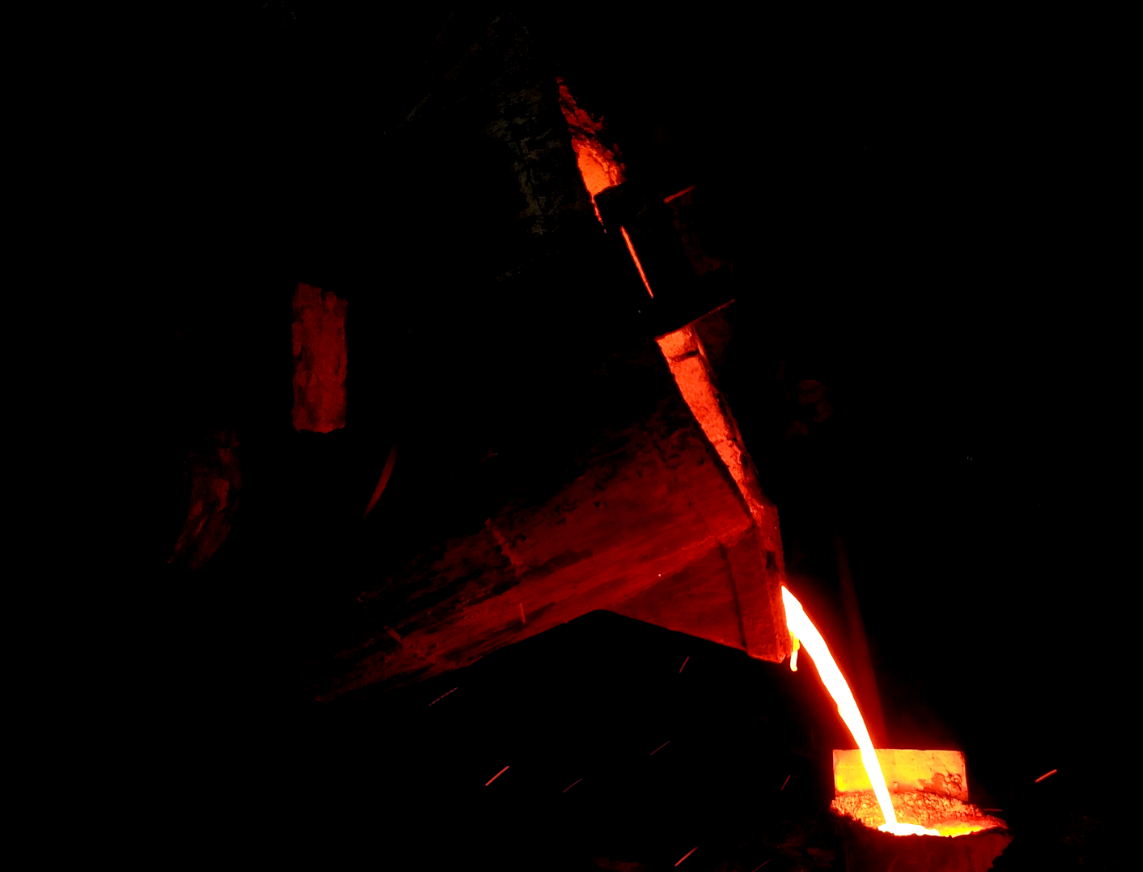

The performance of ductile iron depends on the spheroidization effect of graphite. Medium-frequency furnaces provide the basis of composition and temperature for ductile iron production, but the process has a low tolerance for errors. This article analyzes the three major links of pure smelting, spheroidization treatment, and inoculation process in ductile iron production, clarifying the key parameter boundaries, failure risks, and control strategies of temperature, composition, residual elements, and treatment processes.
2025-11-25 13:53:00
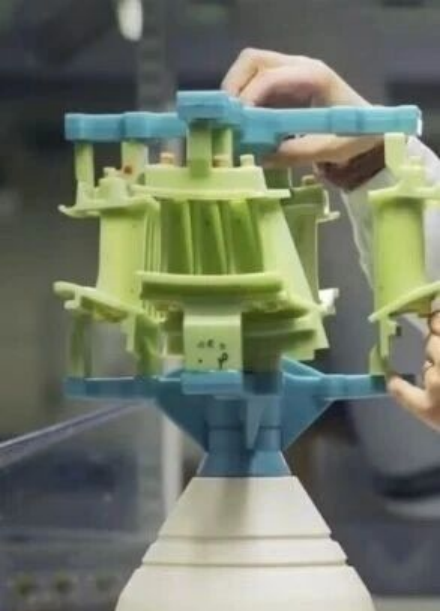

The removal of inclusions in high-temperature alloys is a key technology for improving material performance and promoting recycling, especially crucial in high-end manufacturing fields such as aerospace and energy equipment. Currently, mainstream purification processes can be categorized into three major types: physical separation, melting refining, and emerging composite technologies. The following is a comprehensive analysis of the principles, applicable scenarios, and development trends of each type of technology:
2025-11-25 13:46:25
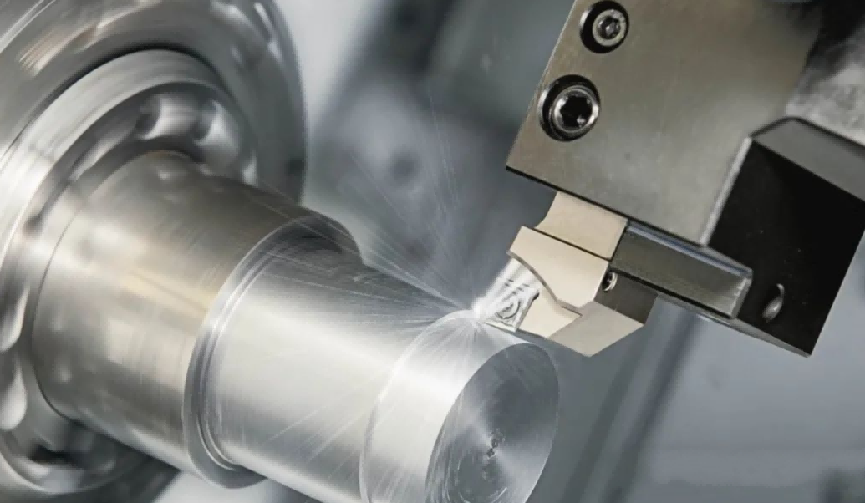

Titanium alloy, with its unique advantages, occupies an important position in aviation, aerospace, medical and other fields. In the past two years, it has also risen in the 3C consumer electronics field, and is used in the body and structural parts of many hot-selling high-end smart phones.
However, the difficult characteristics of titanium alloy processing have been bothering engineers and technicians. This paper will discuss the difficulties of titanium alloy processing and put forward corresponding countermeasures, in order to provide technical support for the wide application of titanium alloy.
2025-11-19 15:54:41
Super austenitic stainless steel 904L is a high-alloy austenitic stainless steel with a low carbon content. It has excellent corrosion resistance in dilute sulfuric acid and is specifically designed for environments with severe corrosive conditions. With a high chromium content and sufficient nickel content, the addition of copper gives it strong acid resistance, especially high resistance to chloride pitting and stress corrosion cracking. It is less prone to corrosion spots and cracks, and has slightly better resistance to pitting corrosion than other steel grades. It has good machinability and weldability and can be used in pressure vessels.
2025-11-19 15:50:56
The die-casting process of the rear end cover of the aluminum alloy motor housing was developed. In the early stage, the runner was reasonably arranged according to the product structure, and the filling and solidification analysis of the gating system was carried out by using numerical simulation software. During the actual production process, it was found that the gas holes in the castings were difficult to eliminate. According to the product structure, different solutions were adopted for different areas. For the gas holes in the thin-walled area at the end of the product where the slag pot could not be arranged, the exhaust insert and the increase of wall thickness were used to improve the fluidity of the aluminum liquid; for the dense gas holes in the thick-walled area at the end of the gating system, the cooling was strengthened to accelerate the local solidification and increase the thickness of the dense layer on the product surface; for the gas holes in the thick-walled area at the feeding port, the gating system was analyzed and the feeding was locally strengthened, etc. The trial production results show that the overall gas holes of the product were improved by using the optimized scheme, and the scrap rate was reduced. Keywords: Motor housing rear end cover; Die-casting process; Numerical simulation
2025-11-13 17:28:42
No matter how good the quality of the finished parts is, the quality of the metal surface treatment can further improve its performance.
In the manufacturing process of metal parts, surface treatment is an indispensable link. Appropriate surface treatment can not only beautify the appearance of metal components but also significantly extend their service life.
2025-11-13 17:14:46

The risers were designed according to the standard. Why are there still shrinkage cavities in the castings?
2025-11-13 17:09:56
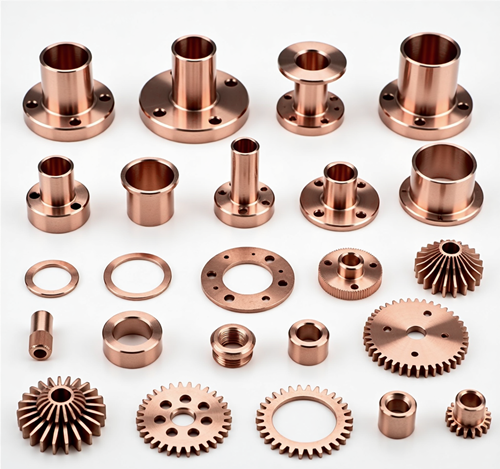

In the field of non-standard mechanical design, copper and copper alloys (such as T2 pure copper, H62 common brass, H59 lead brass, aluminum bronze QAl9-4, white copper B30, beryllium bronze QBe2, and chromium-zirconium copper CuCrZr) have become key materials for special working conditions due to their excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance and processing performance. The rational selection of copper materials can effectively meet the design requirements of electrical conduction, heat conduction, wear resistance and corrosion resistance.
2025-11-13 17:07:20

Titanium alloys are widely used in aerospace, medical, marine engineering and other fields due to their excellent strength, corrosion resistance and biocompatibility. However, the forming process of titanium alloys is complex, and the appropriate forming method needs to be selected according to the shape, size and performance requirements of the parts.
2025-10-30 16:46:57

In mechanical design and materials science, fundamental concepts such as Rigidity, strength, and hardness are essential knowledge that engineers and technicians must master accurately. Although these terms may seem similar, they each have distinct physical definitions and engineering significance. This article will systematically analyze the essential differences among these eight key performance parameters.
2025-10-30 16:39:54
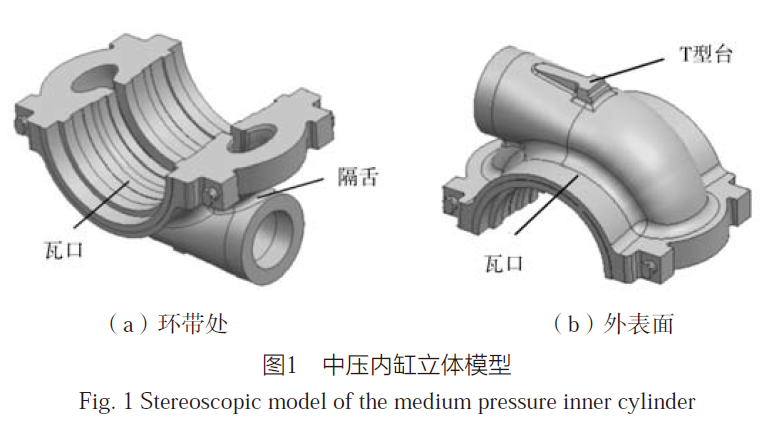
The inner cylinder casting of the steam turbine has a large wall thickness and narrow steam passage in the inner cavity, which is prone to sand sticking. The reasons for the shrinkage porosity defects in the initial casting process were analyzed, and the solidification process was simulated using MAGMA software. The casting process plan was optimized in a targeted manner. After the production verification of the optimized casting process, the casting quality was good and met the technical requirements. Compared with the initial plan, the casting process yield increased by nearly 20%.
2025-10-29 18:04:01
367



