
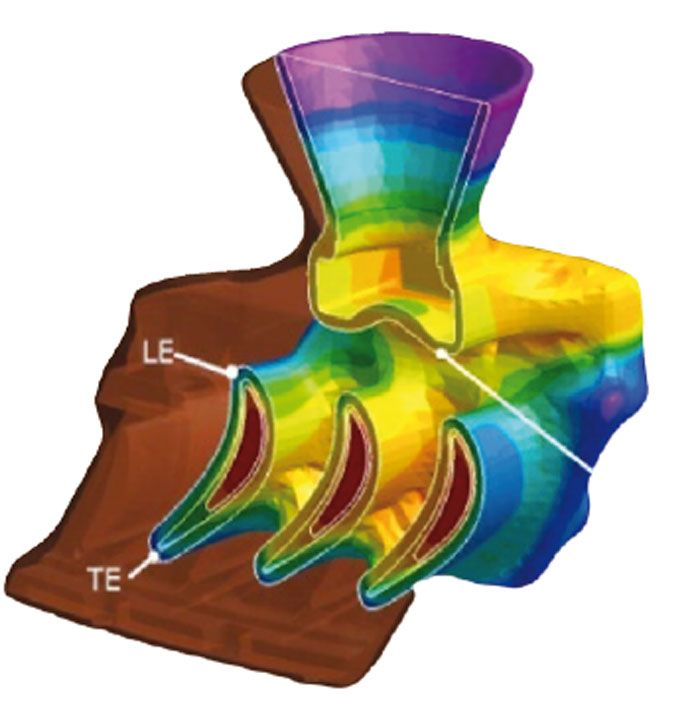
ProCAST is the most advanced investment casting simulation software. It offers a complete set of modules and casting tools to meet all contemporary industrial needs. Based on powerful finite element technology (FEM), ProCAST can predictively evaluate the entire casting process, including filling and solidification defects, mechanical properties, and complex part deformation. It allows for rapid visualization of the impact of design changes and provides a basis for the correct decision-making process from the earliest stages of production. ProCAST enables modeling of all casting processes for all casting alloys and also involves .other related casting production processes, such as core firing and heat treatment. ProCAST Investment Casting simulation software is designed to help users achieve cost reduction and shorten product development time
2025-09-24 17:46:12
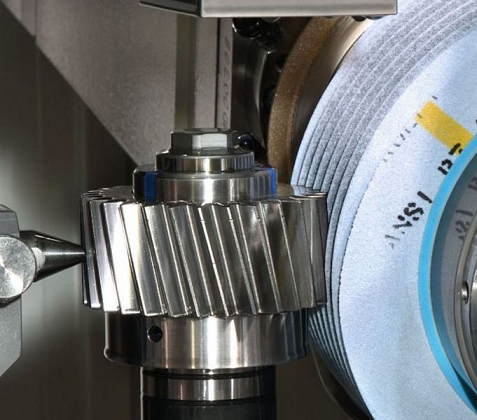

Gear grinding is a precision gear finishing process. It uses a high-speed rotating grinding wheel as the cutting tool to perform fine grinding on the tooth surfaces of gears that have undergone preliminary processing such as hobbing or shaving and have been heat-treated. This process corrects the deformations caused by heat treatment and significantly improves the dimensional accuracy, tooth profile accuracy, and surface quality of the gears. Its core features are high precision and high surface integrity, making it widely used in high-reliability, high-end gear manufacturing fields. Below, we will introduce it from aspects such as working principle, process characteristics, processing equipment, and application scope.
2025-09-24 17:40:20

Stainless steel 304, known for its corrosion resistance, workability, and economic efficiency, is hailed as the "general-purpose stainless steel" and is widely used in food equipment, architectural decoration, medical devices, and other fields. However, in practical applications, users often find that 304 stainless steel still shows rust spots, pitting, or even uniform corrosion under certain conditions. Behind this paradox lies a complex interplay of material science, environmental factors, and surface treatment techniques. This article will analyze the issue from three aspects: the composition characteristics of 304 stainless steel, the causes of corrosion, and the necessity of passivation processes.
2025-09-24 17:38:48

In the world of metal surface treatment, passivation, phosphatization, chromium plating, and anodizing are like four "surface engineers" with distinct personalities, each communicating with metals in their unique chemical language. They either activate the inherent corrosion resistance potential of metals through oxidation reactions or endow metals with new physical properties through deposition and transformation. This article will explore the essential differences among these four surface treatment processes from three dimensions: reaction mechanism, film layer nature, and application logic, revealing their unique positions in materials science.
2025-09-23 17:47:50

Metallic inclusions in steel, as a key defect in the metallurgical process, not only disrupt the continuity of the metal matrix but also significantly reduce material performance through stress concentration effects, crack initiation mechanisms, and other pathways. According to their morphological characteristics and formation mechanisms, metallic inclusions can be classified into three major categories: foreign metal fragments, welding process inclusions, and casting specific structures. Their physical and chemical properties and distribution patterns directly determine the mechanical properties, processing performance, and corrosion resistance of steel.
2025-09-23 17:39:51
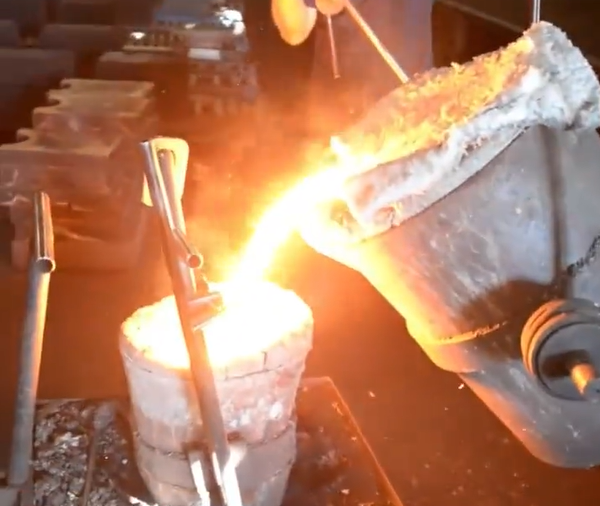

High-performance cast iron (including high-strength gray cast iron and ductile iron) melted in medium-frequency furnaces, due to its pure molten iron, high overheating temperature and large tendency of undercooling during crystallization, poses higher requirements for inoculation treatment. Traditional 75% silicon iron inoculant is prone to deterioration and has limited effect, thus various high-efficiency inoculants have become an inevitable choice.
2025-09-23 17:37:26
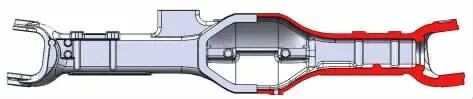
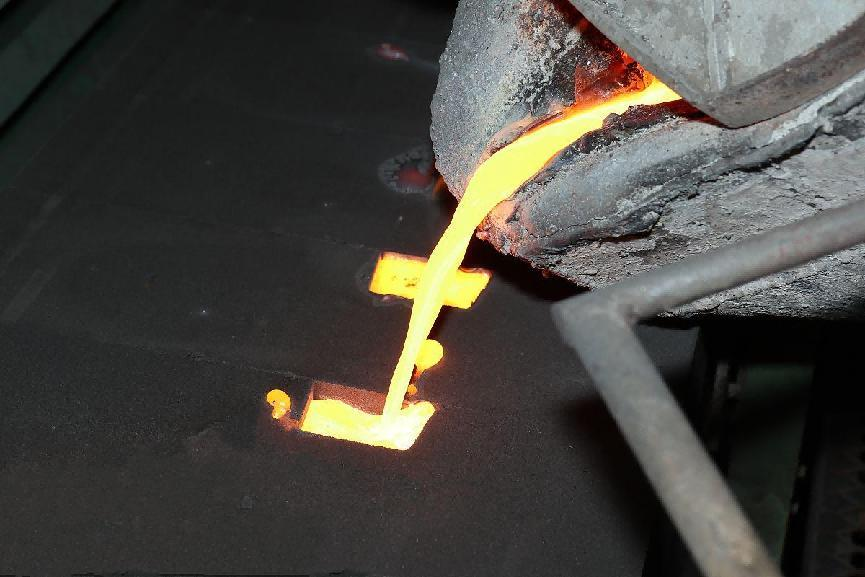
In response to the shrinkage cavity defect in the boss of the integral axle housing support and the deformation in some areas of the casting, the casting process was optimized. The integral axle housing was modeled in 3D using Creo software, and the casting process was simulated using numerical simulation software. The simulation results reflected the locations of shrinkage cavity and porosity defects in the casting. Based on the previous trial production results, the original process plan was optimized. Through the simulation results and the trial production of samples, the optimized plan effectively reduced the shrinkage cavity defects and deformation out-of-tolerance, and improved the product qualification rate.
2025-09-23 17:36:16
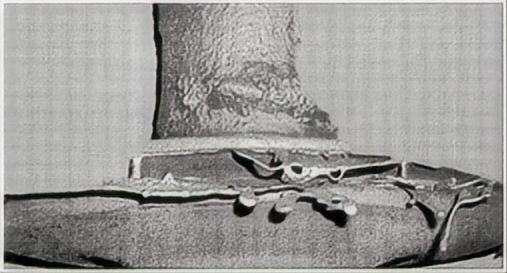
Characteristics: Part of the shell has cracked. After pouring, the molten metal flows out from the cracked area of the shell under the action of dynamic and static pressure, forming irregular and excessive metal on the surface of the casting.
2025-09-23 14:04:11
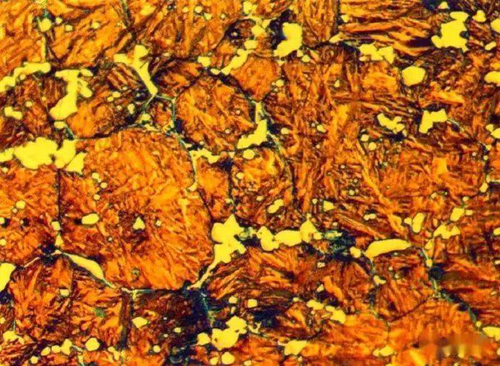
Overburning in heat treatment refers to the phenomenon where the temperature during the heat treatment process is too high, exceeding the melting point of the low-melting eutectic phase in the alloy, causing partial melting of the alloy, resulting in surface nodules and the appearance of remelted phases in the internal structure. Overburning is a serious heat treatment error. Once severely overburned, it cannot be remedied and can only be scrapped.
2025-09-23 14:02:15
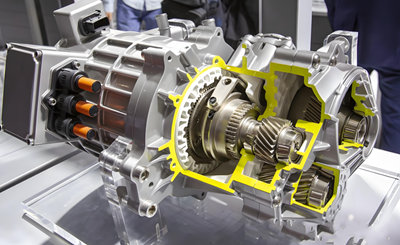
In the context of the electrification era, the electric drive system, as a key component in the fields of new energy vehicles, industrial automation, and renewable energy, is undergoing unprecedented technological innovation. As the core transmission device of the electric drive system, the electric drive gearbox plays a crucial role. This article mainly introduces the working principle, application scenarios, and future development trends of the electric drive gearbox.
2025-09-12 17:13:41

In the field of metallurgy, instantaneous modification technology usually refers to a process method in which specific modifiers are added within an extremely short period of time (typically a few seconds or even less) during the solidification of metals or alloys, causing rapid and significant changes in their microstructure and properties. Different from the traditional modification treatment completed in the furnace, the instantaneous modification technology emphasizes the treatment at the moment of pouring or solidification to ensure that the modifiers can be evenly dispersed and take effect in a timely manner.
2025-09-12 17:10:49
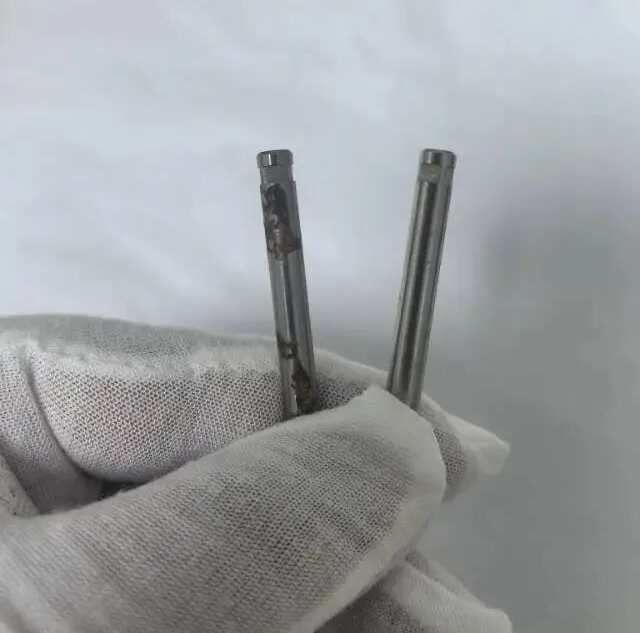

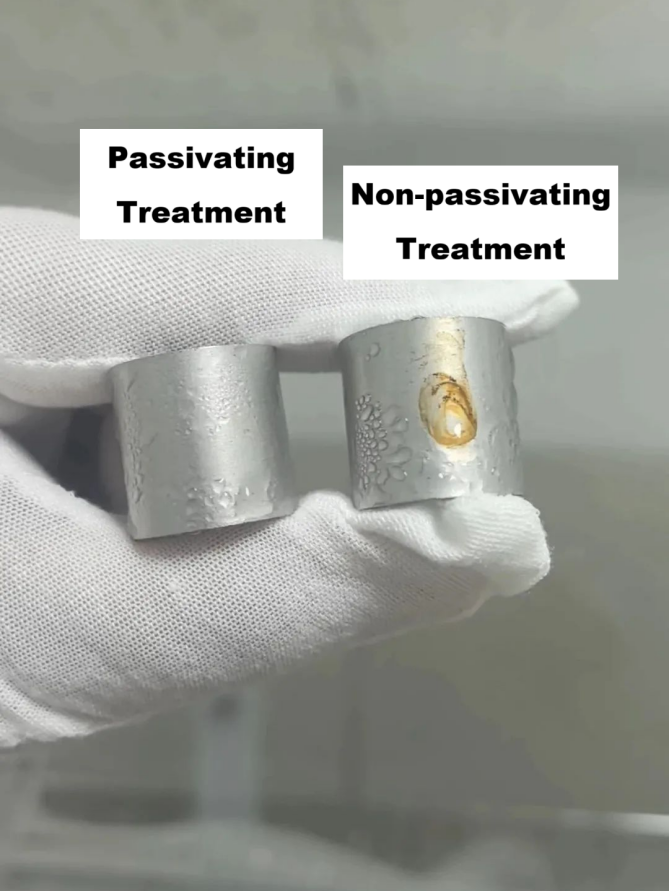
Salt spray testing is a core method for evaluating the passivation effect of stainless steel. By simulating the corrosive environment of marine atmosphere, it verifies the corrosion resistance of the passivation film. However, many enterprises still encounter problems of failing salt spray tests after passivation, manifested as rust spots, white spots or corrosion products on the surface. This article will provide a systematic checklist to analyze the possible causes of test failure step by step, from pre-passivation treatment, passivation process, post-passivation treatment to salt spray test operation, and offer solutions.
2025-09-10 15:07:41
367



