
Ultra-light magnesium-lithium alloy is an ideal material for aerospace and electronic equipment, but its low strength and unstable performance have always restricted its application. The latest research has found that by precisely adding a trace amount of calcium, the strength and plasticity of magnesium-lithium alloy can be simultaneously enhanced, with the yield strength increasing by over 10% and the elongation exceeding 21%!
2025-10-15 18:48:20
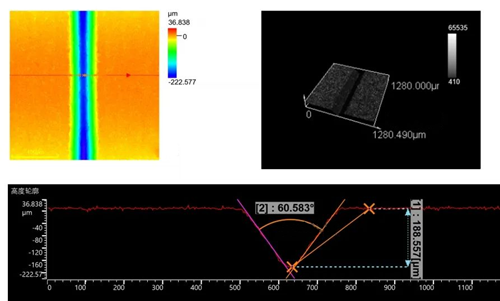
In industrial production, metal components will rub against each other during contact, especially in high-speed or high-frequency sliding and rotating movements, which can easily cause wear due to friction and eventually lead to product scrapping.
2025-10-15 18:45:31

Gears, as the core components in mechanical transmission, the selection of their materials directly affects the transmission efficiency, service life, load-bearing capacity and adaptability to working environments. Different gear materials have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of performance, heat treatment processes and application fields.
2025-10-15 18:41:22

Heat treatment is a crucial stage in the transformation of steel, and quenching, as the most core process among them, directly determines the performance of steel. What is hardening tendency? How does it affect the intrinsic quality of steel? Today, let's delve into this topic.
2025-09-30 17:02:49

When the salt spray test report shows a red "fail" mark, manufacturing enterprises often face delays in product launches, trust crises with customers, and even recall risks. At this point, scientifically and systematically tracing the root cause is more crucial than simply "reworking and retesting". This article will construct a "five-stage, twenty-step" traceability model, which, through a reverse reasoning chain from results to causes, achieves a penetrating analysis from surface problems to essential roots.
2025-09-30 17:00:14
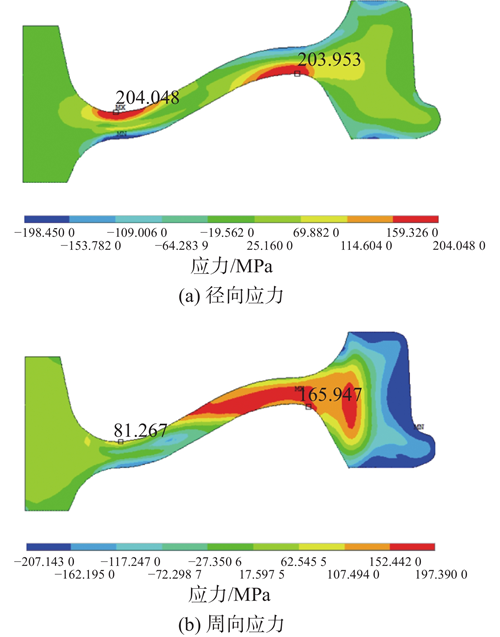
During the processes of casting, welding, heat treatment, and machining of mechanical parts, residual stress - self-balanced internal stress that remains after the removal of external forces or temperature fields - is often generated. If residual stress is not effectively controlled, it can lead to quality issues such as deformation, cracking, and reduced fatigue life, directly affecting the reliability and service life of the product. Therefore, mastering systematic and feasible stress relief methods is an essential skill in mechanical design and manufacturing.
2025-09-30 16:57:32

The defects of flash and burrs usually appears in the form of a straight or zigzag line and often occurs on the curved surfaces, edges, and corners of castings, as well as the inner corners of elbow products. The most direct cause is that the shell has cracks before pouring. During pouring, the molten steel seeps out along the cracks, similar to the process of "fire running" in the inner cavity, but the formation mechanism is different. Most of these cracks occur during the dewaxing process.
2025-09-25 18:15:10

Alloy 59 (ASTM B575 N06059) is a high-purity nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloy, renowned for its outstanding corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability, making it a crucial material in the chemical, energy, and other industries. The following is a detailed analysis of its specific properties and applications.
2025-09-25 18:13:26
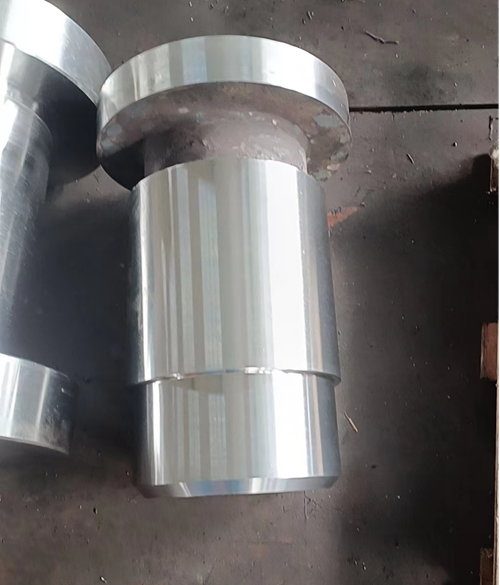

UNS NO6600 alloy is a Ni-Cr alloy that can be used in a temperature range from cryogenic to 1093℃. UNS NO6600 alloy is non-magnetic and has good weldability. UNS NO6600 alloy can be used in a wide range of corrosive environments. The high nickel content gives 600 alloy certain corrosion resistance in reducing environments, while the addition of chromium gives 600 alloy certain corrosion resistance in weakly oxidizing environments. Due to its relatively high nickel content, 600 alloy has excellent corrosion resistance to chloride stress corrosion cracking. The formability of 600 alloy is similar to that of stable austenitic stainless steel.
2025-09-25 18:10:37
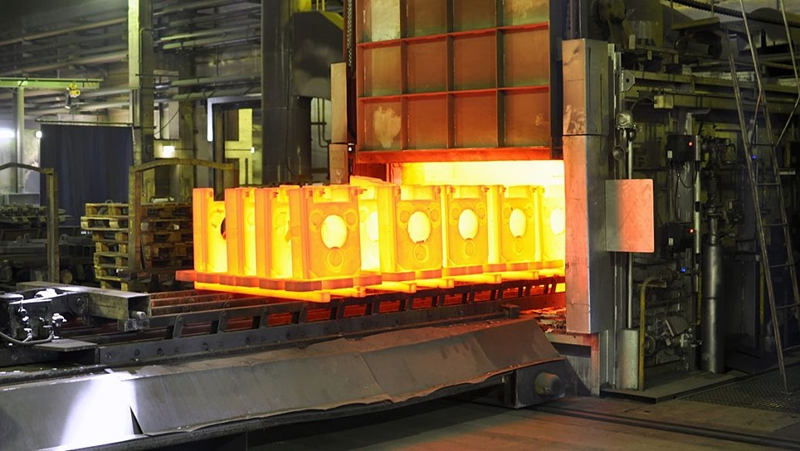

Heat treatment refers to a metal thermal processing technique in which materials are heated, held at a certain temperature, and then cooled while in the solid state to achieve the desired microstructure and properties. Simply put, it involves "four fires": normalizing, annealing, tempering, and quenching. Its functions are as follows:
2025-09-25 17:45:22
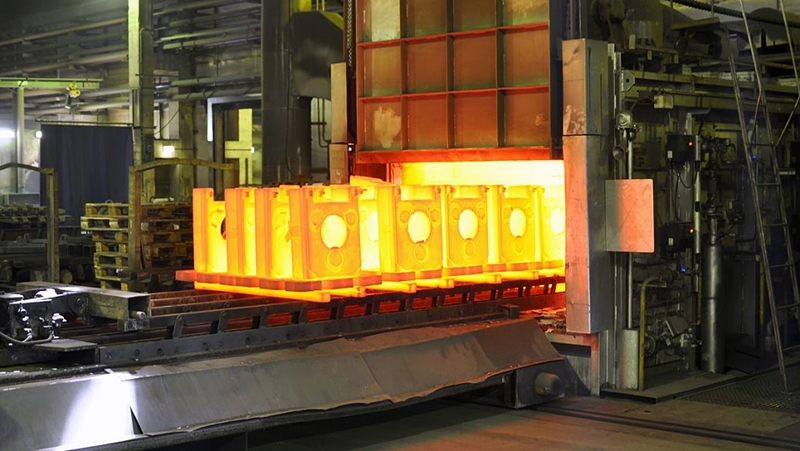

Heat treatment is a crucial process that alters the internal structure of metal materials through heating, holding at a certain temperature, and cooling to achieve the desired properties.
2025-09-24 18:00:26

The bottleneck of traditional heat dissipation materials
2025-09-24 17:55:03
367



