
Knowledge
Super Stainless Steel - Fully Austenitic 904L
Super austenitic stainless steel 904L is a high-alloy austenitic stainless steel with a low carbon content. It has excellent corrosion resistance in dilute sulfuric acid and is specifically designed for environments with severe corrosive conditions. With a high chromium content and sufficient nickel content, the addition of copper gives it strong acid resistance, especially high resistance to chloride pitting and stress corrosion cracking. It is less prone to corrosion spots and cracks, and has slightly better resistance to pitting corrosion than other steel grades. It has good machinability and weldability and can be used in pressure vessels.
Performance
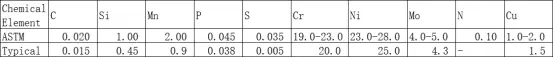
1. 904L Chemical Element
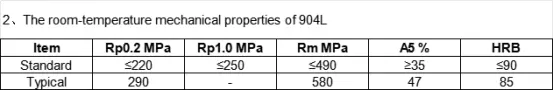
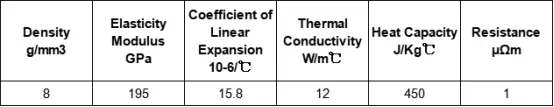
Physical properties of 904L
• Density: 8.00 g/cm³
• Melting point: 1300 - 1390 ℃
• Tensile strength: σb ≥ 520 MPa
• Elongation: δ ≥ 35%
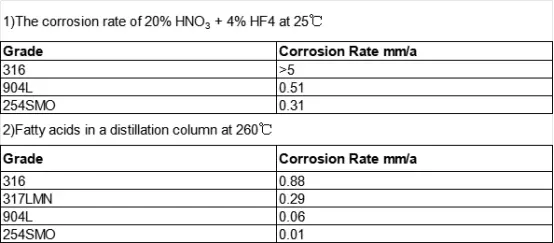
Corrosion resistance
Production and processing performance
1) Welding performance
Like general stainless steel, 904 L can be welded by various welding methods. The most commonly used welding methods are manual arc welding or inert gas shielded welding. The electrode or wire metal is based on the composition of the base material and has a higher purity, with a higher molybdenum content than the base material. Generally, preheating is not required before welding, but in cold outdoor operations, to avoid water vapor condensation, the joint area or adjacent areas can be uniformly heated. Note that the local temperature should not exceed 100°C to avoid carbon accumulation and intergranular corrosion. During welding, it is advisable to use a small heat input, continuous and fast welding speed. Generally, no heat treatment is required after welding. If heat treatment is necessary, it should be heated to 1100-1150°C and then rapidly cooled.
2) Machining performance
The machining characteristics of 904 L are similar to those of other austenitic stainless steels. During the machining process, there is a tendency for the tool to stick and for work hardening to occur. Positive rake angle hard alloy tools should be used, and sulfurized and chlorinated oils should be used as cutting coolants. The equipment and process should be designed to minimize work hardening. Slow cutting speeds and feed rates should be avoided during the cutting process.
Application fields
Petroleum and chemical industry
Reactors, heat exchangers, pipelines, etc., perform outstandingly in handling strongly corrosive fluids such as sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid.
Flue gas desulfurization
Flue ducts, absorption towers, and spray systems in flue gas desulfurization systems of power plants can withstand high temperatures and corrosive exhaust gases.
Marine engineering
Commonly used in seawater treatment systems and ship components, it has outstanding resistance to crevice corrosion and stress corrosion.



