

(1) Characteristics: There are numerous small pitted holes on the surface of the casting, with diameters ranging from 0.3 to 0.8 mm and depths of 0.3 to 0.5 mm. This defect often occurs on alloy steel castings with low carbon content and w(Cr) ranging from 5% to 18%. Before cleaning, the shallow pits are filled with slag-like substances.
(2) Causes: The pitting is mainly caused by chemical reactions between metal oxides and oxides in the shell material.
(3) Locations: On the local or entire surface of the casting, with more occurrences in thin-walled areas.
(4) Illustration: See Figure 1.
2025-08-13 17:45:14
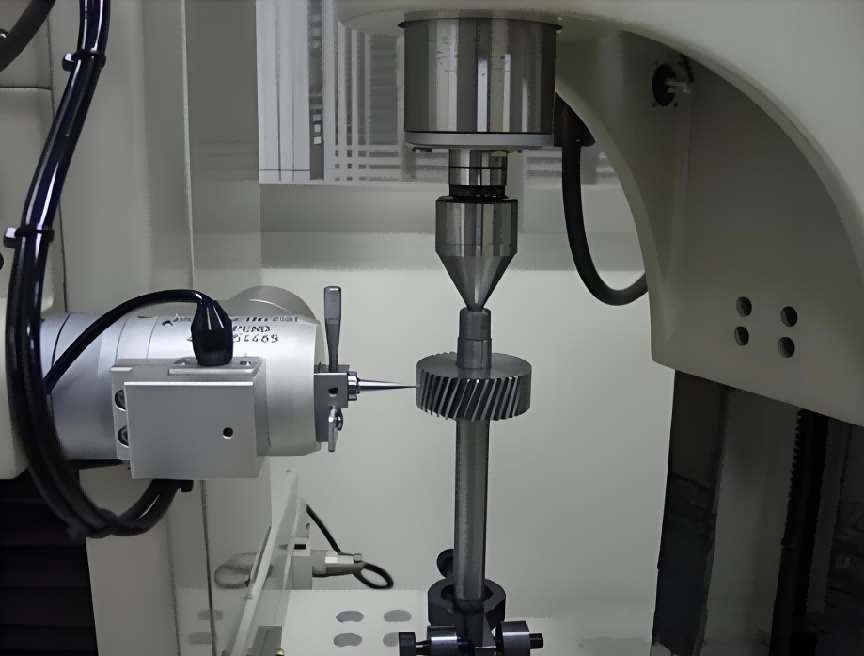

This article elaborately describes the meaning of gear accuracy, its evaluation system and control methods, and conducts a detailed analysis of the mainstream international accuracy standards such as ISO, AGMA and DIN. It also explores the accuracy control strategies and detection technologies in the gear manufacturing process, providing theoretical guidance and technical references for gear design and manufacturing.
2025-08-07 17:03:30
Gears are the core components of mechanical transmission systems, and their reliability directly affects the operational life and safety of equipment. However, under high-speed, heavy-load or harsh working conditions, gears often fail due to various reasons, such as fracture, leading to equipment downtime or even safety accidents. Pitting is also a common failure mode of gears, which can reduce transmission efficiency, increase noise, and even cause complete gear failure.
2025-08-07 16:53:42
Copper has excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, ductility and certain strength. Adding various alloy elements to copper can improve its corrosion resistance, strength and improve its machinability.
2025-08-07 16:46:54

Among all the cast metals, gray cast iron is the most versatile. It has many desirable properties that no other casting alloy possesses, and it is the cheapest iron material that can be effectively utilized. Among iron alloys, gray cast iron has the lowest pouring temperature, which can be verified by its good fluidity and casting ability when pouring complex cavities. Due to its unique solidification mechanism, gray cast iron has very low or even no liquid or solid phase shrinkage, making it easy to obtain qualified castings. Compared with iron alloys of the same tensile strength, gray cast iron has better machinability and vibration damping capacity, higher thermal conductivity, and good corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance, and wear resistance.
2025-08-06 16:53:56
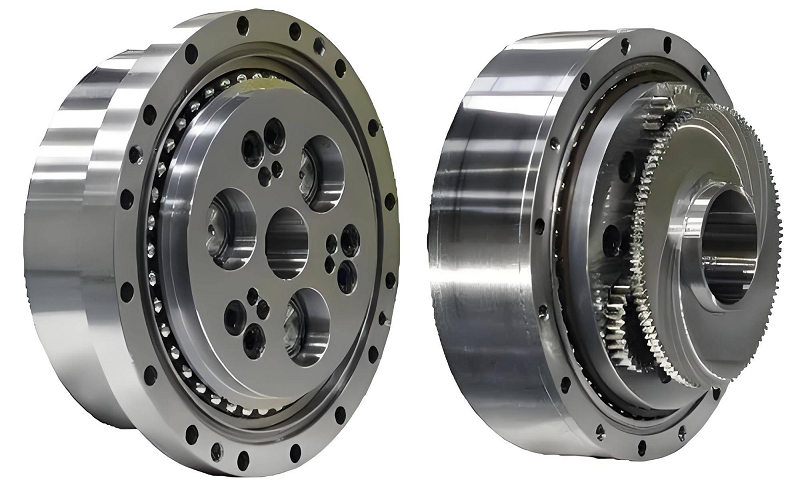

In the fields of automated equipment, industrial robots, and precision machine tools, reducers are like the precise gear hearts, silently transmitting power and precision. Faced with various types of reducers: harmonic, RV, planetary, and cycloidal, how to choose? Who will lead the future? This article analyzes the four major reducer technologies one by one to help you clarify your direction in the selection of technical paths.
2025-08-06 16:49:13
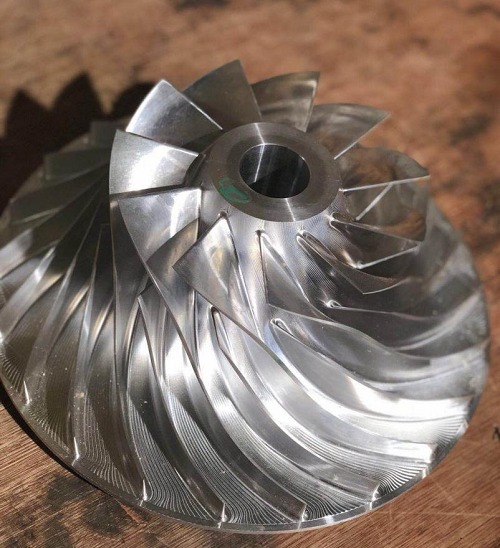

The moving parts of a centrifugal compressor are the key components for achieving gas compression and energy conversion. Their performance directly affects the efficiency, stability and service life of the entire machine. This article will systematically review the main moving parts in a centrifugal compressor and their functions.
2025-08-01 18:27:39
Strategic Partnership and Long-Term Agreements: Establish long-term strategic partnerships with key suppliers (such as steel, bearings, seals, cutting tools, etc.) to secure more favorable prices and more stable supplies.
Introduce Competition and Price Comparison: For non-strategic materials or standard parts, maintain 2-3 qualified suppliers to promote healthy competition.
Joint Purchasing/ Centralized Purchasing: If multiple departments within the company require the same type of materials, centralized purchasing should be carried out to enhance bargaining power.
Local Purchasing: Under the premise of ensuring quality and delivery time, give priority to local suppliers to reduce logistics costs and risks.
2025-07-31 00:00:00
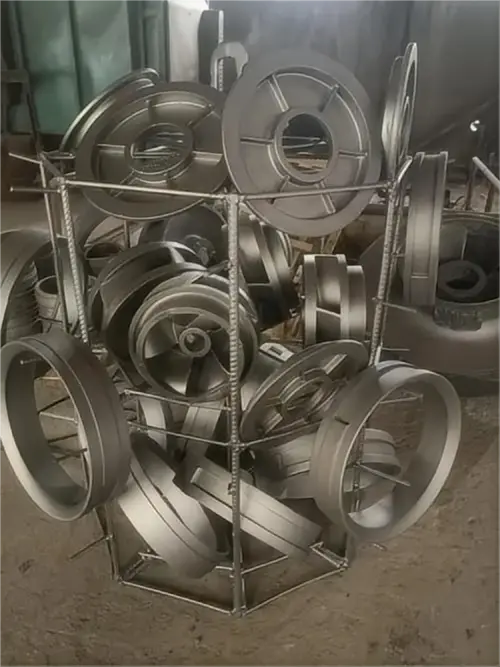

K418 (international designation IN713C) is a nickel-based precipitation-hardened equiaxed grain cast superalloy specifically designed for high-stress and corrosive environments below 900°C. As a core material for China's aero-engine and energy equipment, it achieves a balance among high-temperature strength, thermal fatigue resistance, and environmental tolerance through γ' phase strengthening and high-chromium corrosion resistance design. It is particularly suitable for environments containing corrosive media such as sulfur and chlorine. This report systematically analyzes the composition design principles, performance advantages, manufacturing techniques, and future challenges of K418 alloy.
2025-07-30 16:09:17
Reducing the manufacturing cost of gearboxes is a systematic project that requires optimization from multiple aspects such as design, materials, processes, procurement, production management, and supply chain. The following are some key strategies and specific methods:
2025-07-30 16:06:38

904L steel is a high-grade austenitic stainless steel. Its unique composition provides outstanding performance and durability, making it an ideal choice for applications in the chemical, marine, and other demanding environments.
2025-07-30 13:27:32
367



