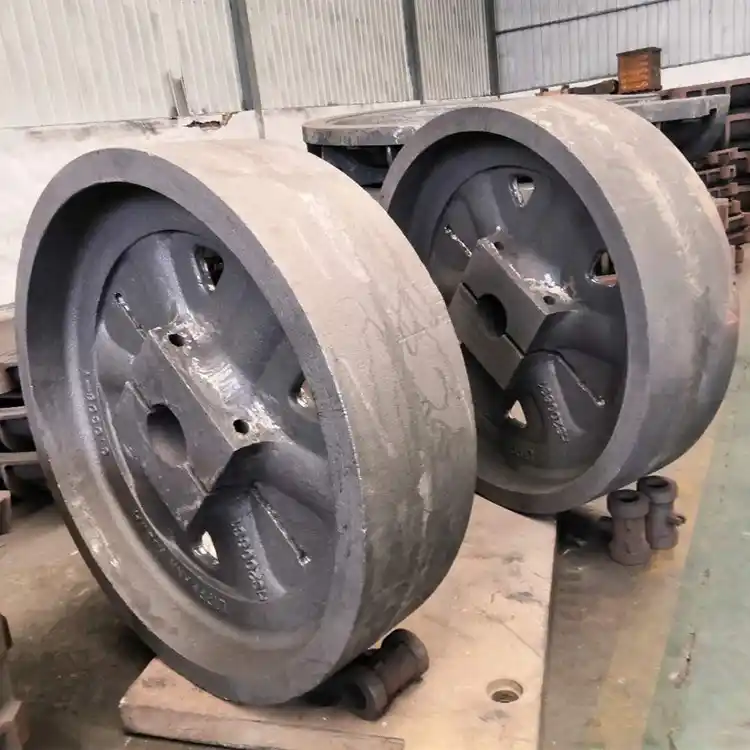


There are many types of large ductile iron castings, such as large diesel engine blocks, large wheel hubs, large ball mill end covers, blast furnace cooling walls, large steel rolling mill frames, large injection molding machine templates, large turbine bearing housings, wind turbine hubs and bases, and nuclear waste tanks, etc. In addition to meeting the mechanical properties specified in the standards, these components also have some special performance requirements, such as low-temperature impact toughness for wind power castings and many additional special acceptance standards for nuclear waste tanks, etc. Therefore, when producing these castings, thorough consideration must be given in advance.
2025-09-10 15:01:13
Steel, as a core material in modern industry, has its properties determined by the 28 elements dissolved or precipitated in the iron matrix. These elements significantly influence the strength, toughness, corrosion resistance and processability of steel through mechanisms such as solid solution strengthening, second phase precipitation and grain boundary regulation. This paper systematically reviews the action mechanisms of major elements such as carbon, silicon and manganese, as well as trace elements like boron, niobium and titanium, and reveals the scientific laws of element synergy design by combining application cases of typical steel grades.
2025-09-10 14:51:22
_1756714885309.png)

The spline part of the spline shaft exhibited a "deformation" phenomenon. After inquiry, the shaft showed a phenomenon of torsional neck contraction but had not yet fractured.
2025-08-29 15:16:00
The utilization of steel by humans can be traced back to the Iron Age of the 12th century BC. At that time, people discovered through experience that prolonging the heating time of iron ore in a charcoal furnace would make the iron harder, and they developed the quenching hardening technique. Ancient India had mastered the technology of producing Uzh steel in the 3rd century BC. This is a type of crucible steel with a carbon content between pig iron and wrought iron, and its outstanding performance enabled it to be exported all over the world. However, these early steel production methods mostly relied on generations of passed-down experience, and the underlying scientific principles remained shrouded in mystery.
2025-08-29 15:06:00
This paper briefly describes the structural features, technical requirements and manufacturing difficulties of heavy ductile iron castings. It elaborates on the casting methods, gating system design methods and manufacturing methods of this type of castings. The process characteristics, production advantages and application scope of resin sand solid mold casting are introduced. Through strict process control, selection of appropriate raw materials, proper spheroidizing and inoculation treatment processes, and special pretreatment techniques during the production process, high-quality large ductile iron castings can be produced. This can provide technical references for the solid mold casting process of similar heavy castings.
2025-08-27 15:32:17
Pitting refers to small and shallow pits that appear in the contact area of gear teeth surfaces. These pits are usually formed due to local material spalling. At the beginning of pitting, they are generally tiny spots. With the passage of time and the continuous action of load, these spots gradually expand, deepen, and connect with each other, forming larger areas of spalling, which seriously affects the working performance of gears.
2025-08-27 15:20:42
To correctly consider feeding and gating, it is necessary to understand alloy solidification. The solidification mechanisms of different alloys can vary significantly. Therefore, the methods for producing dense and defect-free castings also differ. This article considers some basic factors that influence the solidification pattern and discusses how these factors affect the design methods of risers and gates.
2025-08-27 15:16:59

The gating system of castings is mainly responsible for transferring clean and slag-free molten steel from the ladle to the mold cavity without causing secondary oxidation or gas absorption. To some extent, all alloys are affected by slag formation, and some, such as aluminum-based and copper-based alloys, are particularly susceptible.
2025-08-27 15:13:13
To ensure stable product quality during batch manufacturing, this model is processed and controlled with full numerical control for high-precision machining, further enhancing the accuracy and stability of the model's dimensions. The model is also subjected to three-dimensional data detection to comprehensively inspect all its dimensions and shapes, ensuring its quality and precision. This is crucial for batch manufacturing of castings and can effectively prevent casting quality issues caused by model errors. The three-dimensional model is illustrated in Figure 9, and the three-dimensional detection data is shown in Figure 10.
2025-08-27 15:06:10
After analyzing the part structure, material properties, technical requirements and casting process difficulties of the CB2 main steam valve regulating valve shell casting, as well as considering potential casting quality issues, through the research on the cause of valve shell cracks, solidification zone feeding and the setting of cold iron in the solidification end zone, the common defects such as porosity and cracks in the casting process were effectively solved. A reasonable and practical casting process plan was developed, and the control of the manufacturing process was strengthened, improving the stability of the process and operation. After production verification, the overall quality of the valve shell was good, meeting the standard requirements, and the batch manufacturing of the CB2 main steam valve regulating valve shell was successfully achieved.
2025-08-27 15:04:18
What kinds of steel are used for gear nitriding? And some microstructure characteristics of commonly used steels. Understanding the microstructure characteristics can help to bring out the good performance of gears in use, and at the same time optimize the gear manufacturing process, which is conducive to improving the service life of gears.
2025-08-13 17:48:37
367



