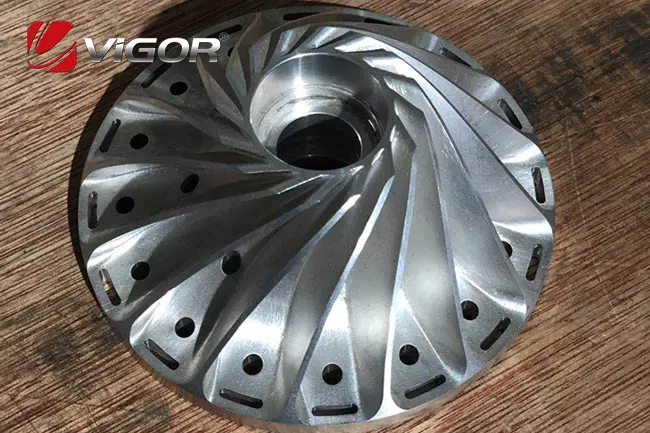


Aerospace-grade turbocharger impellers are revolutionizing the world of high-performance engines, offering unmatched efficiency, durability, and precision. Designed to withstand extreme conditions, these components are the backbone of advanced turbocharging systems, enabling peak engine performance in industries ranging from automotive to aerospace. With cutting-edge engineering, rigorous material selection, and innovative manufacturing processes, aerospace-grade impellers are setting new benchmarks for power, speed, and reliability. At VIGOR INNO-TECH Limited, we specialize in crafting these high-quality components with over 18 years of expertise in castings, forgings, and custom production solutions for global customers.
2025-02-21 09:39:07
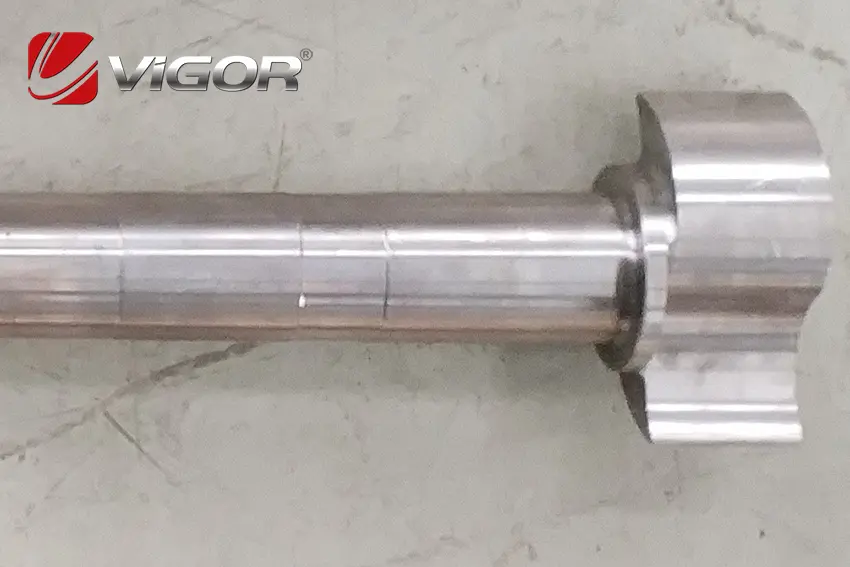

When it comes to high-performance vehicles and industrial machinery, the brake camshaft is a critical component that ensures optimal braking efficiency and safety. For OEMs requiring tailored solutions, custom brake camshaft manufacturing offers a way to meet specific performance and application requirements. At VIGOR INNO-TECH Limited, we specialize in delivering precision-engineered brake camshafts, leveraging over 18 years of experience in casting and forging. Our expertise lies in understanding the unique needs of our OEM clients, designing durable, high-performing brake camshafts, and ensuring the best combination of quality, cost-effectiveness, and production efficiency. In this blog, we'll explore the benefits of custom brake camshaft solutions, the critical considerations for OEMs, and how VIGOR INNO-TECH's expertise ensures superior results for our global partners.
2025-02-21 09:38:51
The CNC processing technology knowledge is elaborated in the following six sections:
1. Introduction to CNC processing and its key characteristics
2. Important elements of CNC processing
3. CNC processing parameters
4. Common post-processing steps in CNC processing
5. Basic structural design for CNC processing
6. Preliminary assessment of manufacturability for CNC processing
2025-02-20 18:06:24

In the field of mechanical engineering, choosing the right materials is crucial for ensuring the performance, reliability and cost-effectiveness of products. Mechanical engineers need to have a thorough understanding of the properties, applications and limitations of various materials in order to make informed decisions during the design and manufacturing process. The following are 20 commonly used materials that mechanical engineers must know, including both metallic and non-metallic materials, each accompanied by a brief description.
2025-02-20 17:48:44
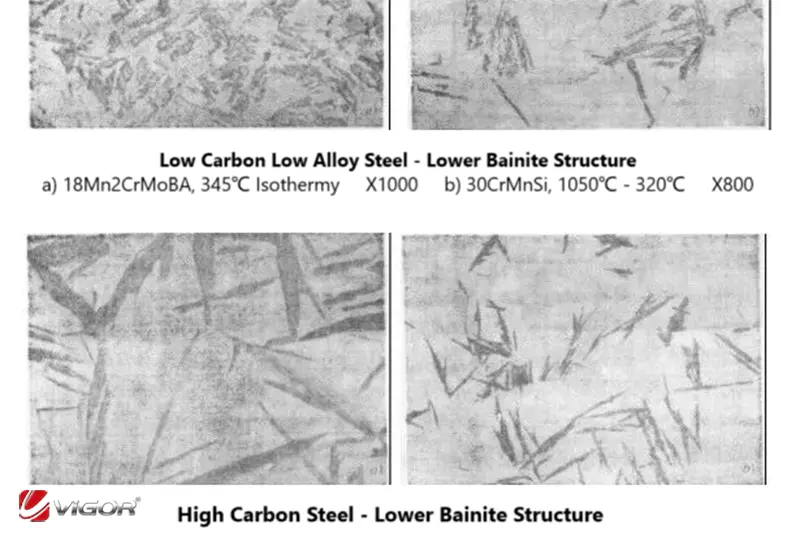
In the field of materials science, lower bainite and high carbon martensite are two important metal microstructures, which have significant differences in microstructure characteristics, mechanical properties, and application fields. This article will detail the main differences between these two microstructures.
2025-02-20 17:36:06
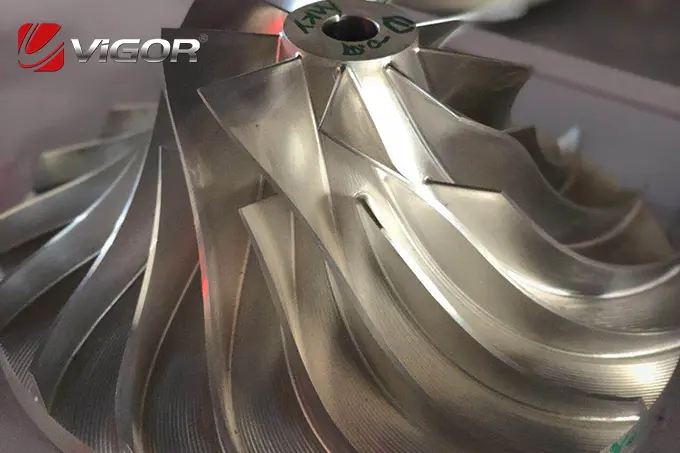

Ensuring quality in turbocharger impeller manufacturing is critical for achieving high performance, durability, and efficiency in modern engines. Turbocharger impellers operate under extreme conditions, requiring precise design and robust production processes to meet demanding performance standards. At VIGOR INNO-TECH Limited, we leverage over 18 years of expertise in casting and forging, combined with advanced quality control systems, to deliver impellers that exceed customer expectations. This blog explores the key aspects of quality assurance in turbocharger impeller manufacturing and how VIGOR ensures excellence at every stage of production.
2025-02-19 09:31:03
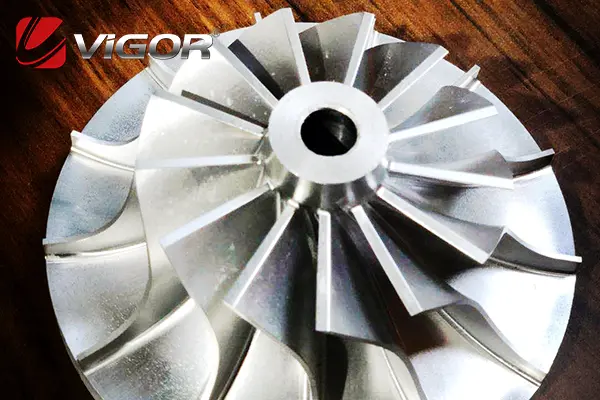

Marine turbocharger impellers play a crucial role in maintaining the performance and reliability of marine engines, even under the most challenging conditions. Designed to withstand extreme temperatures, high pressures, and corrosive environments, these components are vital for optimizing fuel efficiency and ensuring uninterrupted operation during voyages. With proper design, material selection, and manufacturing expertise, turbocharger impellers can significantly enhance the durability and efficiency of marine engines. This article explores the importance of turbocharger impellers, the factors influencing their design and production, and how VIGOR INNO-TECH Limited offers customized solutions for your specific needs.
2025-02-19 09:30:56
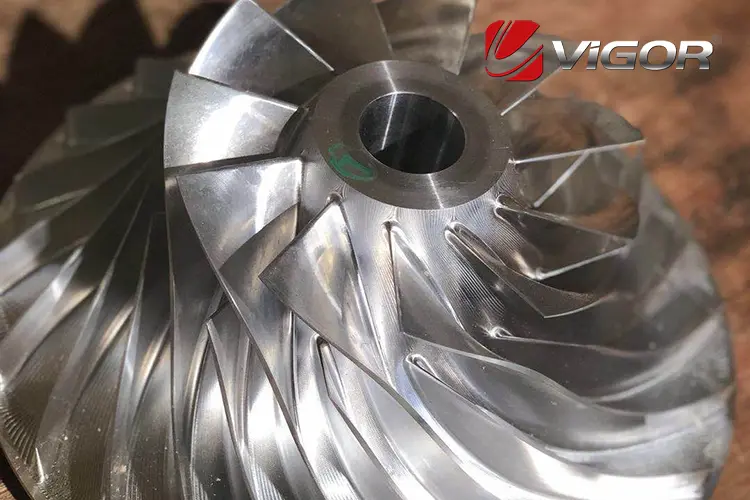

Choosing the right turbocharger impeller supplier is critical to the performance, durability, and efficiency of turbocharged systems. A reliable supplier ensures not only high-quality parts but also timely delivery and expert technical support. With so many options available globally, identifying a supplier who aligns with your technical, economic, and logistical requirements can significantly impact the success of your business. Below, we'll explore the key considerations to help you make an informed decision.
2025-02-19 09:30:50

A worn-out brake camshaft is a significant concern for vehicles and machinery relying on braking systems. Symptoms of a failing brake camshaft include unusual noises during braking, uneven braking performance, difficulty in applying brakes, and excessive wear on brake components. Ignoring these signs can lead to serious safety risks and costly repairs. This guide will help you identify the common symptoms of a worn-out brake camshaft, understand its causes, and outline preventive measures to extend its lifespan.
2025-02-19 09:29:24

Precision die forging is revolutionizing the production of brake camshafts, offering unparalleled quality, performance, and durability. Brake camshafts play a critical role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of heavy-duty vehicles, making their precision and reliability essential. Through advanced die-forging techniques, manufacturers can produce brake camshafts with superior structural integrity, reduced material waste, and optimized performance for the most demanding applications. With VIGOR INNO-TECH's 18+ years of expertise in castings and forgings, we deliver excellence in brake camshaft production, ensuring unmatched quality and efficiency for our global customers.
2025-02-19 09:29:14
_1740034814477.webp)
The brake camshaft plays a critical role in ensuring proper brake adjustment by transferring the force from the brake pedal to the brake shoes or pads. This component rotates when the brake pedal is pressed, causing the brake shoes to press against the drum or rotor, creating the friction necessary to slow down or stop a vehicle. If a brake camshaft is worn, misaligned, or damaged, it can lead to uneven braking, reduced efficiency, and even unsafe driving conditions. Ensuring the brake camshaft is in optimal condition is key to maintaining precise brake adjustments and overall vehicle safety.
2025-02-19 09:29:05
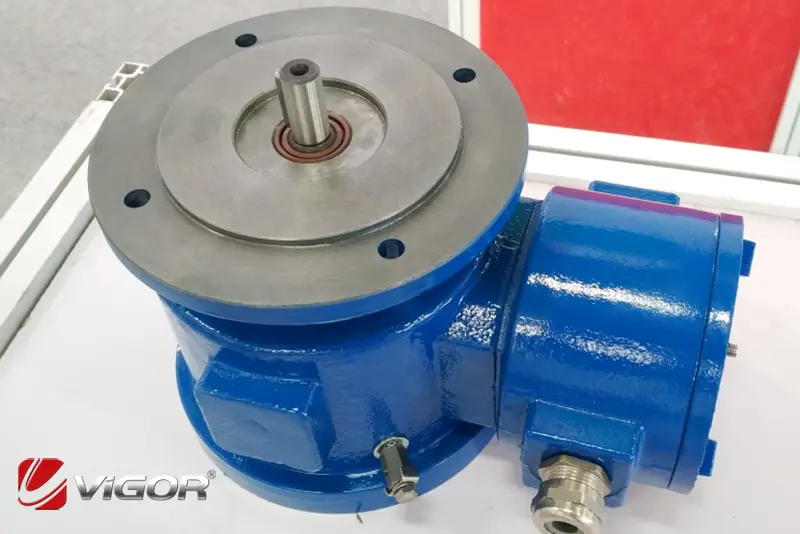

Electric motor brakes can be classified into various types based on their working principles and application scenarios, each with its own unique characteristics. The following are some common types of electric motor brakes and their features:
2025-02-18 17:41:13
367



