
There are many basic parameters for shot blasting. The common ones include shot blasting intensity (the requirements for shot blasting and shot peening in parameter control are the same, so shot peening is used to represent both shot blasting and shot peening in the following text), shot blasting coverage, surface roughness of the workpiece, and surface cleanliness of the workpiece.
2025-12-11 09:43:21
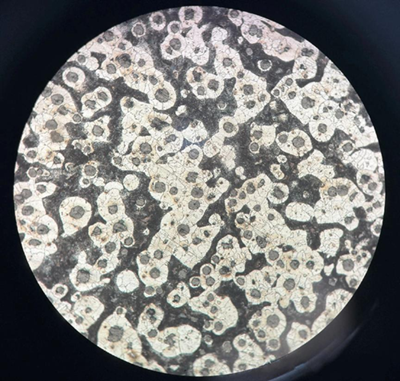
The illustration shows the typical microstructure morphology of ductile iron. The black dots in the picture represent the "spherical graphite" of the lamellar structure; the black patches represent "pearlite"; the bright and uniform structure formed around the carbon-poor areas of the spherical graphite in the picture is "ferrite".
2025-12-11 09:41:34
I'd like to share with you the technical literature "An overview of ceramic molds for investment casting of nickel superalloys", which is probably the most comprehensive review on ceramic shell research at present.
2025-12-11 09:36:40
The strengthening of metals includes solid solution strengthening, strain strengthening and dispersion strengthening. The following is an introduction to dispersion strengthening.
2025-12-04 18:08:45

Forming technology of wrought magnesium alloys alters the microstructure of magnesium alloys through plastic processing methods such as extrusion, rolling, and forging, significantly improving their mechanical properties such as strength and ductility. This technology is suitable for manufacturing structural components with high reliability requirements, such as automotive chassis and aircraft engine blades. However, due to the hexagonal close-packed crystal structure of magnesium alloys, they have only one slip system at room temperature, resulting in extremely poor plasticity. Therefore, magnesium alloys are usually heated to 200 - 450℃ for hot working to improve their formability. The forming technology of wrought magnesium alloys mainly includes the following types:
2025-12-04 18:06:29

In the fields of mechanical design, equipment manufacturing, transmission systems, and non-standard automation, 45 steel, 40Cr, and 42CrMo are the three most commonly used structural steels. Although they may seem similar at first glance, their chemical compositions, mechanical properties, responses to heat treatment, and application scenarios are quite different. Selecting the wrong material can lead to shortened service life at best and direct failure at worst. This article systematically dissects the differences among the three from an engineering application perspective and tells you how to make the right selection.
2025-12-04 18:02:25
Heat treatment is an important method to improve the performance of metal materials. Cold treatment, as an extension and supplement to heat treatment, plays a significant role in enhancing the hardness, tensile strength and dimensional stability of workpieces. This article mainly introduces the basic principles, process flow, applicable materials and application scope of cold treatment.
2025-12-03 15:23:51

Perform stress relief heat treatment on key processing components (i.e., those prone to deformation or large-sized parts), especially molds. Stress relief is carried out at a temperature of approximately 550°C to 660°C. Usually, it is applied before hardening, with the aim of minimizing tension, but it is also recommended to use it after final mechanical processing. Annealing is typically performed on processed raw material parts to obtain a structure with low hardness, good cold plasticity, and good machining performance for machine tools. Specifically:
2025-12-03 15:22:54
In order to produce cast ductile iron parts with stable performance at low cost, our company once collaborated with a university to conduct research on copper-manganese alloyed cast ductile iron. The results were published in the journal "Foundry" that year.
2025-12-03 15:12:59
Due to the poor thermal conductivity, high alloy content, narrow forging temperature range and high processing difficulty of 9Cr18Mo stainless steel, it is very easy to cause coarse forging structure and twin structure due to excessively high forging temperature and too long holding time. Twin structure has extremely strong heredity and stability, and it is difficult to eliminate through annealing and quenching treatment. Therefore, process tests were conducted on 9Cr18Mo stainless steel bearing parts with forged twin structure to study the feasibility of removing the forged twin structure of 9Cr18Mo stainless steel bearing parts through heat treatment methods.
2025-12-01 14:30:57
PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition, physical vapor deposition) is a coating technology that deposits films on the substrate surface by converting the material source (target) into gaseous particles (atoms, molecules or ions) through physical methods in a vacuum environment. The core principle is to use vacuum conditions to reduce the scattering of gas molecules on the deposited particles, allowing the particles to move in a straight line to the substrate, thereby achieving controlled film growth.
2025-12-01 14:13:42

Common Quenching Defects of Steel and Preventive Measures
2025-12-01 13:39:17
367



