
Knowledge
Gear Accuracy (I)

This article elaborately describes the meaning of gear accuracy, its evaluation system and control methods, and conducts a detailed analysis of the mainstream international accuracy standards such as ISO, AGMA and DIN. It also explores the accuracy control strategies and detection technologies in the gear manufacturing process, providing theoretical guidance and technical references for gear design and manufacturing.
Basic Concepts of Gear Accuracy
1.1 Definition and Importance of Accuracy
Gear accuracy refers to the degree of conformity between the geometric parameters of a gear pair and the ideal design parameters. It directly affects:
Transmission smoothness (vibration and noise level)
Load-carrying capacity (contact spot distribution)
Transmission efficiency (power loss)
Service life (wear uniformity)
1.2 Classification of Precision Elements
According to the ISO 1328 standard, gear precision includes three aspects:
Individual deviation, cumulative deviation, and tooth surface quality.
Gear accuracy standards
2.1 Comparison of mainstream standards
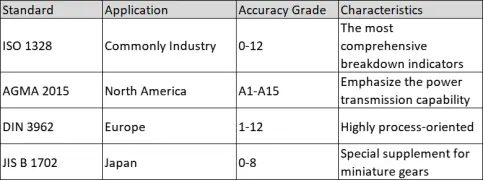
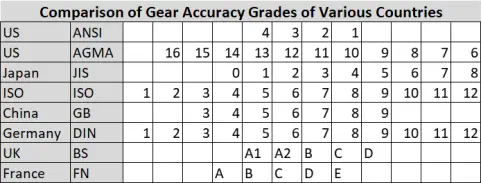
2.2 Core
Parameters of ISO 1328
Gear accuracy inspection items:
Pitch deviation (Fp, fpt, Fpk)
Flank deviation (Fα, fHα)
Helix deviation (Fβ, fHβ)
Radial runout (Fr)
Tooth profile error (Fα, fHα) reflects the deviation between the actual tooth profile of a gear and its ideal shape, which is of great significance for evaluating the performance and quality of the gear. Tooth profile error indicates the deviation between the actual tooth profile of a gear and its ideal shape, and it is an important indicator for assessing the performance and quality of the gear.
The tooth alignment accuracy (Fβ, fHβ) affects the transmission performance and service life. Gear tooth alignment accuracy that meets the standard requirements can reduce noise and vibration. It directly influences the transmission performance and service life of gears. Through precise control of tooth alignment accuracy, it can ensure that gears remain stable during transmission, reduce noise and vibration, and thereby extend their service life.
Pitch deviation (Fp, fpt, Fpk) reflects the uniformity of the distance between gear teeth and is of great significance for ensuring the transmission accuracy and stability of gears. The detection of pitch deviation ensures the accuracy and stability of gear transmission, and precise data is obtained through a pitch measuring instrument. The main methods for detecting pitch deviation include measurement with a pitch measuring instrument and obtaining the deviation value by comparing with the standard pitch.
Radial runout (Fr) directly affects transmission accuracy and smoothness.
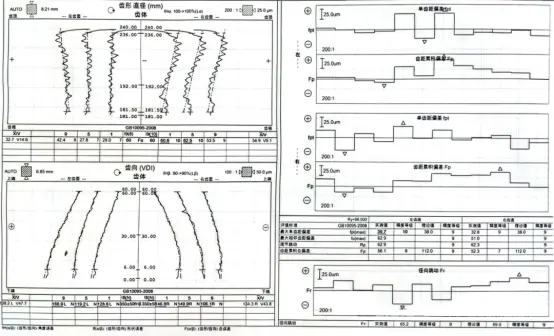
The specific precision values can be referred to the standard "GBT10095.1-2008".
Gear accuracy characteristics:
Motion accuracy - It refers to the deviation between the actual transmission ratio and the theoretical transmission ratio of gears during the transmission process. In a transmission system, high-precision motion transmission is the key to ensuring the stability and reliability of the mechanical system. Deviations in motion accuracy can lead to changes in the transmission ratio, increased wear on the tooth surface, and subsequently cause vibration and noise. In severe cases, it may even affect the overall performance of the system.
Contact accuracy - refers to the contact condition between the tooth surfaces of gears, including contact area, contact pressure and contact form, etc. Good contact accuracy can ensure that gears have uniform load distribution and high load-bearing capacity during transmission, thereby prolonging the service life of gears.
Smoothness - The smoothness of gears during the transmission process refers to the impact and vibration conditions when gears mesh. The smoothness accuracy of gears is influenced by multiple factors, including pitch deviation, tooth profile error, and base pitch deviation etc. It is required that the instantaneous speed ratio variation of gear transmission be within the design range. Improving the smoothness accuracy can effectively reduce vibration, impact, and noise during the transmission process, enhancing the reliability and comfort of the system.
Precision grade selection suggestions:
Automobile gearboxes: 4-6 grades
Industrial reducers: 7-8 grades
Agricultural machinery gears: 9-10 grades
Vigor has rich experience, a professional team, and the advanced equipment in producing the Die-forged high quality and high accurate gears and the shafts. If any thing we can help or any new parts need to be developed, please contact us at info@castings-forging.com



