
Knowledge
What are the Main Materials of the Impellers for Centrifuges and Centrifugal Compressors?
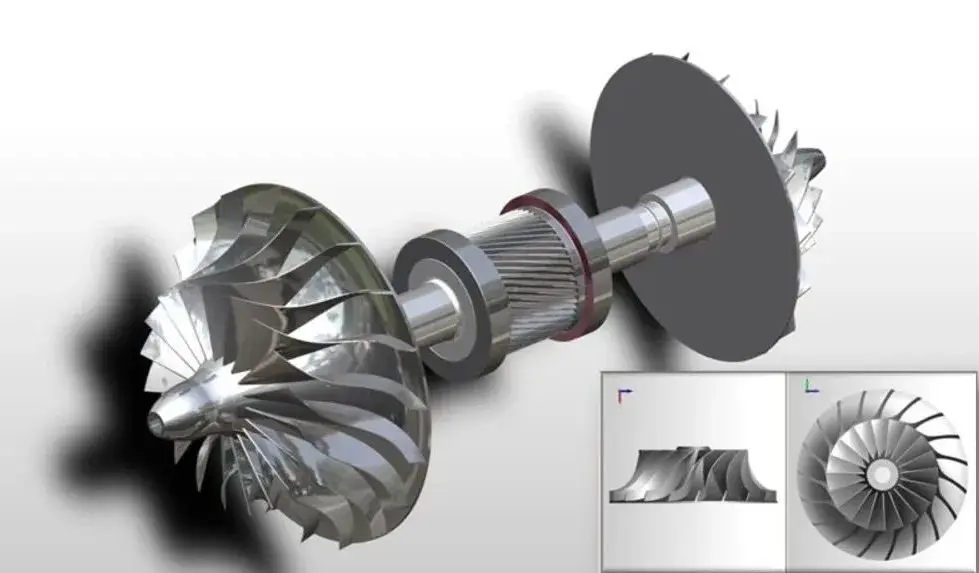
The impeller of a centrifugal compressor plays a core role in its structure, and the material selection of the impeller directly affects the performance, lifespan and applicable working conditions of the equipment. The impeller is installed on the horizontal pinion shaft inside the gearbox. In the figure below, each end of the pinion shaft is equipped with an impeller, which is a common configuration. However, it is equally common to have only one impeller installed on each pinion shaft.
Air enters from the center of the top of the impeller, drives the air and accelerates it through the blades, guiding it to the lower end of the blades, and is ultimately thrown out along the tangent at the end of the blades. This increase in air velocity is the initial process by which pressure is raised in a centrifugal compressor.
The depth, length and angle of the impeller blades are key factors for aerodynamic engineers to design compressors to achieve different performances. In addition, the material strength and material usage of the impeller are also crucial, as the rotational speed of these impellers can reach up to 30,000 RPM or even higher. Obviously, at such high speeds, blade breakage is absolutely unacceptable, as it would lead to the complete destruction of the compressor.
In modern engineering and manufacturing fields, these impellers are typically machined from a single piece of raw material blank using a five-axis milling machine to achieve the precise characteristics designed by engineers based on the performance requirements of end users.
The impeller design has dual objectives: it must meet the required flow and pressure characteristics while also providing the compressor with the best efficiency in terms of energy demand. Therefore, excellent engineering design can create the most reliable and efficient compressor.
The raw material can be carbon steel, stainless steel, or in some cases, special materials selected based on the specific gas handled by the compressor. High-end centrifugal compressors used for compressed air typically employ stainless steel rather than carbon steel to extend the service life of components.
Depending on different operating conditions and conveyed media, impellers are usually made of metal materials with high strength and corrosion resistance. The following are several common impeller materials and their technical characteristics.
Stainless steel materials (such as 17-4PH, 13Cr) are widely used in general-purpose centrifugal compressors, especially in conditions where corrosion resistance is required. These materials have good strength and processing performance, and they are chemically inert in most industrial gas environments, making them a cost-effective choice.
Titanium alloy materials (such as Ti-6Al-4V)
Titanium alloys are widely used in compressor equipment in high-end fields such as aerospace and marine platforms due to their excellent strength-to-weight ratio and outstanding corrosion resistance. Although they are relatively expensive and difficult to process, they have obvious advantages in systems with extremely high requirements for weight and reliability.
Aluminum alloy materials (such as 7075-T6, 2024)
Aluminum alloys are suitable for applications where weight is a concern and pressure is relatively low. They are characterized by their light weight and ease of processing, but have relatively low strength and fatigue life, and are not suitable for corrosive gas media. Therefore, they are typically used in situations with lower performance requirements, such as low-pressure air compression systems.
Nickel-based alloy materials (such as Inconel 718, Monel) have excellent high-temperature strength and creep resistance, making them suitable for high-temperature and high-pressure applications, especially in the compression of petroleum, natural gas, and chemical process gases. These materials perform well in oxidizing and corrosive environments, but they are relatively expensive and have high processing costs.
Duplex or super duplex stainless steel
In corrosive media containing chloride ions or hydrogen sulfide, duplex stainless steel demonstrates outstanding resistance to stress corrosion cracking and is suitable for harsh conditions such as sour gas. It combines excellent mechanical properties with superior corrosion resistance, making it a highly desirable material.
The selection of impeller materials should take into account the following factors comprehensively:
- The composition and corrosiveness of the gas being conveyed
- The operating pressure and temperature of the compressor
- Whether there are weight or high-speed rotation restrictions
- Fatigue life and usage frequency
- Cost control and the feasibility of processing and manufacturing
In actual engineering practice, material selection should follow industry standards such as API 617 or the specifications provided by the compressor manufacturer (OEM) to ensure the safety and reliability of the equipment.
Vigor has professional 5-axis machining centers and the team to produce high-accuracy impellers for centrifuge and centrifugal blower, and turbocharger, etc. If you have questions or any impellers need to be developed, please feel free to contact us at info@castings-forging.com



