Knowledge
How To Choose a Type of Casting Process?
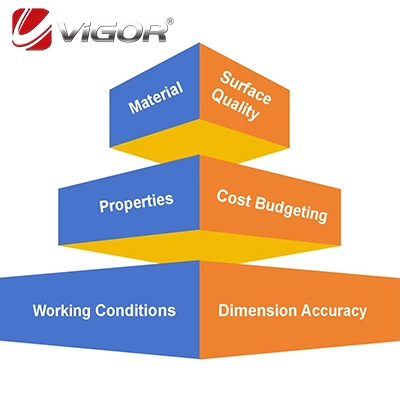
Considerations for selecting an appropriate casting process include: material, complexity, quantity, and desired properties. Investment casting works well for complex designs, while die casting is best for mass-producing metal parts. For larger components, sand casting is more affordable, whereas precision casting offers tighter tolerances. Centrifugal casting works best for cylindrical objects, while gravity casting is appropriate for simpler shapes. To make an educated decision, assess the requirements of your project.
What Is the Most Popular Type of Casting?
One of the most well-liked and widely employed casting techniques in manufacturing is sand casting. All industries prefer it because of its flexibility, efficiency, and capacity to create complex shapes. The adaptability of sand casting in terms of material choices and mold design, as well as its suitability for both small- and large-scale production, contribute to its widespread use in industries like automotive and aerospace.
What Are the Materials Used in Casting?
Materials used in casting include:
- Metals: Such as iron, aluminum, copper, and zinc.
- Alloys: Combining metals to enhance properties, like bronze and brass.
- Ceramics: Like porcelain and clay for pottery.
- Plastics: Including thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics.
- Composite materials: Mixing fibers and resins for specialized applications.
- Rubber: For creating flexible parts.
- Glass: Used for artistic and functional objects.
- Concrete: Common in architectural and decorative casting.
Is Metal Used in Casting?
Yes, casting does often incorporate metal. Metal is cast by pouring molten metal into a mold to create different shapes and objects. It is one of the most commonly employed casting materials because of its adaptability, toughness, and variety of uses in sectors like: construction, aerospace, and automotive. To learn more, see our guide on Metalloid Uses.
Is Polyethylene Used in Casting?
Yes, polyethylene is used in casting, and more specifically, polyethylene cast films are used. These films are made using a cast extrusion method, in which plastic resins, such as polyethylene, are melted and created into thin films by being extruded through a slit die. These films find use in a variety of industries, including: packaging, agriculture, and construction. To learn more, see our guide on PE Plastic.
What Differentiates Casting From Injection Molding?
Injection molding involves pushing melted material (most commonly plastic) into a mold under high pressure, as opposed to casting, which broadly involves pouring molten material into a mold and waiting for it to solidify. A wider variety of materials, including metals, and larger, more complex shapes are suitable for casting. For smaller parts, injection molding offers high precision and is an affordable option for mass production. Both approaches have specific benefits, and in some manufacturing processes, they can work well together. To learn more, see our guide on the Process of Molding.
At Vigor, our mechanical department boasts a team of seasoned engineers with extensive experience in the forging and casting industry. They provide robust technical backing for our products, ensuring top-notch quality and performance. Our expert team offers a variety of casting processes and comprehensive advice on design and manufacturing.
If you're interested in superior casting and forging machinery products, don't hesitate to contact us. Discover how our exceptional technical expertise and high-quality products can meet your needs with excellence.